10.1B: Searching a SQLite Database
Contents:
- What you should already KNOW
- What you will LEARN
- What you will DO
- App overview
- Task 0. Download and run the base code
- Task 1. Add a Search Menu Item
- Coding challenge
- Summary
- Related Concept
- Learn More
What you should already KNOW
For this practical you should be familiar with:
- SQLite databases
- Writing basic SQLite queries
What you will LEARN
You will learn to:
- Add search functionality to your app via the options menu
- Build search queries for the SQLite database from user input.
What you will DO
In this practical you will add an item to the options menu for searching the database, and an activity that allows users to enter a search string and displays the result of the search in a text view.
Why: Users should always be able to search the data on their own terms.
Note: The focus of this practical is not optimizing the UX of the search request, but showing you how to query the database.
App Overview
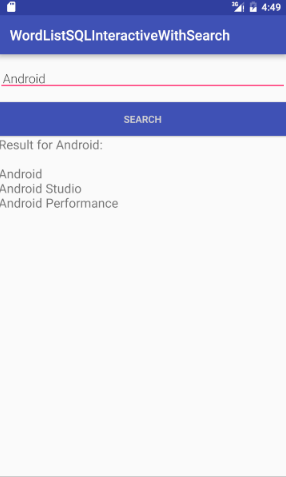
You will make a copy of the finished WordListSQLInteractive app (or WordListSqlStarterCode if you didn't rename it; from a previous practical), call it WordListSQLInteractiveWithSearch, and add an activity that lets users search for partial and full words in the database. For example, entering "Android" will return all entries that contain the substring "Android".
Task 0. Download and run the base code
In order to save you some work, this practical will build on an app you have already built. In a production environment, building on existing application code is a common developer task to add features or fix problems.
1. Create your project
Download the WordListSQL finished app.
You can use your own app, or download the base app. As long as the app uses a SQLite database, you can use these instructions to extend it.
- Load a copy of the app into Android Studio. Refer to the Appendix for information on copying a project.
- Rename the package using Refactor > Rename.
- Change the package name in your build.gradle file.
- Run the app to ensure it builds and functions correctly.
Task 1. Add Search
1.1. Add an Options Menu with Search item
Use the OptionsMenuSample code from your previous practicals if you need an example of how to do this.
- In your project, create an Android Resource directory and call it menu with "menu" as the resource type (res > menu).
- Add a main_menu.xml menu resource file to res > menu.
Create a menu with one item Search. Reference the code snippet for values.
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" tools:context="com.android.example.wordlistsqlsearchable.MainActivity"> <item android:id="@+id/action_search" android:title="Search..." android:orderInCategory="1" app:showAsAction="never" /> </menu>- In MainAcvitiy, inflate the menu by overriding onCreateOptionsMenu.
@Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu); return true; } - Override onOptionsItemSelected method. Switch on action_search, and just return true.
@Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { switch (item.getItemId()) { case R.id.action_search: return true; } return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); } - Run your app. You should see the dots for the options menu. When you click it, you should see one menu item for search that does nothing.
1.2. Create the layout for the search activity
This layout is similar to activity_edit_word, so you can take advantage of existing code and copy it.
- Create a copy of activity_editword and call it activity_search.xml.
- In activity_search.xml, change the id's and strings to be representative of searching.
- Change the onClick method for the button to showResult.
- Add a TextView with an id of search_result, at least 300dp height, and 18sp font size.
- Run your app. You should notice no difference.
1.3. Add an Activity for searching
- Create a new activity, SearchActivity. If your create it by New > Android > Activity then DON'T generate the layout file because we created it in the previous task.
- Add a private TextView class variable mTextView.
- Add a private EditText class variable mEditWordView.
- Add a private WordListOpenHelper variable mDB.
- In onCreate, initialize mDB with a new WordListOpenHelper(this).
In onCreate, initialize mTextView and mEditWordView to their respective views.
public class SearchActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = EditWordActivity.class.getSimpleName(); private TextView mTextView; private EditText mEditWordView; private WordListOpenHelper mDB; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_search); mEditWordView = ((EditText) findViewById(R.id.search_word)); mTextView = ((TextView) findViewById(R.id.search_result)); mDB = new WordListOpenHelper(this); } }- Add the activity to the AndroidManifest.
<activity android:name="com.android.example.wordlistsqlsearchable.SearchActivity"> </activity>
1.4. Trigger SearchActivity from the menu
- To start SearchActivity when the menu item is selected, insert code to start SearchActivity into the switch statement in the onOptionSelected() method in MainActivity.
Intent intent = new Intent(getBaseContext(), SearchActivity.class); startActivity(intent); - Build and run your app to make sure SearchActivity is launched when the "Search" menu item is selected from the OptionsMenu.
- Enter a search string and press "Search". Your app crashes.
- Find out why the app has crashed, then move to the next task.
1.5. Implement the onClick handler for the Search button in the SearchActivity
Your app crashed, because the onClick handler set for the Search button in the XML code doesn't exist yet. So you will build showResult next.
When the Search button is pressed, several things need to happen:
- The event handler calls public void showResult(View view) in SearchActivity.
- Your app has to get the current value from the mEditWordView, which is your search string.
- You print the "Result for" and the word in mTextView.
- You call the (not yet written) search function on mDB (mDB.search(word) and get back a SQlite database cursor. You will implement the search function in the next task.
- You process the cursor and add the result to mTextView.
- In SearchActivity, create the showResult function. It is public, takes a View argument, and returns nothing.
- Create a
Stringvariable calledwordand initialize it with the contents of the input edit text view,mEditWordView. - Show the search term in the search results TextView; something like
"Search term: " + word - Search the database and get the cursor.
Cursor cursor = mDB.search(word); To process the cursor, you need to do do the following:
Make sure the cursor is not null.
Move the cursor to the first entry.
Iterate over the cursor processing the current entry, then advancing the cursor.
Extract the word.
Display the word in the text view.
- Close the cursor.
- If no results are found, the user sees a blank screen with no results. You would want this to be handled in a production app.
Check the annotated code for additional details.
public void showResult(View view){ String word = mEditWordView.getText().toString(); mTextView.setText("Result for " + word + ":\n\n"); // Search for the word in the database. Cursor cursor = mDB.search(word); // Only process a non-null cursor with rows. if (cursor != null & cursor.getCount() > 0) { // You must move the cursor to the first item. cursor.moveToFirst(); int index; String result; // Iterate over the cursor, while there are entries. do { // Don't guess at the column index. // Get the index for the named column. index = cursor.getColumnIndex(WordListOpenHelper.KEY_WORD); // Get the value from the column for the current cursor. result = cursor.getString(index); // Add result to what's already in the text view. mTextView.append(result + "\n"); } while (cursor.moveToNext()); // Returns true or false cursor.close(); } // You should add some handling of null case. Right now, nothing happens. }Your app will not run without at least a stub for search() implemented. Android Studio will create the stub for you. In the light bulb, choose create method.
- Open WordListOpenHelper.
- Implement a stub for search, with a String parameter, that returns a null cursor.
- Run your app and fix any errors you may have. Note that most of the code in showResult() is not exercised yet.
1.6. Implement the search method in WordListOpenHelper
The final step is to implement the actual searching of the database.
Inside the search() method, you need to build a query with the search string and send the query to the database.
A more secure way to do this is by using parameters for each part of the query.
WHY: In the previous practical, for the query in WordListOpenHelper, you could build the query string directly and submit it as a rawQuery(), because you had full control over the contents of the query. As soon as you are handling user input, you must assume that it could be malicious.
You will learn more about security in the Security chapter and Security Tips.
The SQL query for searching for all entries in the wordlist matching a substring has this form:
SELECT * FROM WORD_LIST_TABLE WHERE KEY_WORD LIKE %searchString%;
The parametrized form of the query method you will call looks like this:
Cursor query (String table, // The table to query
String[] columns, // The columns to return
String selection, // WHERE statement
String[] selectionArgs, // Arguments to WHERE
String groupBy, // Grouping filter. Not used.
String having, // Additional condition filter. Not used.
String orderBy) // Ordering. Setting to null uses default.
See the SQLite Database Android and the documentation for various query()) methods.
For the query in the search() method, you need to assign only the first four arguments.
- The table is already defined as the
WORD_LIST_TABLEconstant. - In search(), create a variable for the columns. You need only the value from the
KEY_WORDcolumn.String[] columns = new String[]{KEY_WORD}; - Add the % to the searchString parameter.
searchString = "%" + searchString + "%"; - Create the where clause. Omit "WHERE" as it's implied. Use a question mark for the argument to LIKE. Make sure you have the correct spacing.
String where = KEY_WORD + " LIKE ?"; - Specify the argument to the where clause, which is the searchString.
String[] whereArgs = new String[]{searchString}; - Add a Cursor cursor variable and initialize it to null.
In a try/catch block.
Get a readable database if mReadable is not set yet.
Query the database using the above form of the query. Pass null for the unused parameters.
Handle the exception. You can just log it.
- Return the cursor.
- Run your app and search for some strings.
Here is the solution for the complete method:
public Cursor search (String searchString) {
String[] columns = new String[]{KEY_WORD};
searchString = "%" + searchString + "%";
String where = KEY_WORD + " LIKE ?";
String[]whereArgs = new String[]{searchString};
Cursor cursor = null;
try {
if (mReadableDB == null) {mReadableDB = getReadableDatabase();}
cursor = mReadableDB.query(WORD_LIST_TABLE, columns, where, whereArgs, null, null, null);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.d(TAG, "SEARCH EXCEPTION! " + e);
}
return cursor;
}
Solution code
Android Studio project: WordListSqlSearchable
Coding challenges
- Handle the case where no results are found in a more user-friendly way.
Most of the code samples use the default AppBar that comes with the Empty Template. In some of the previous chapters, you learned about the Toolbar, for example, when using the Basic Template.
Change the app to use the Toolbar and SearchView and show the search icon on the toolbar.
https://developer.android.com/training/search/setup.html
https://developer.android.com/training/appbar/setting-up.html
- As written, this app is not very secure. Consider how to add basic input validation for the search string. See Security Tips.
Summary
- An options menu can be an effective UI for searching a SQlite database
- A separate activity to handle the UX for search can help focus the user
- In a production application, SQlite queries should be managed carefully to avoid data corruption or security issues
- SQLite search queries can be constructed dynamically using user input for the query parameters.
- The query() method searches a database for matching words.
- The query() method returns a database cursor which can traverse the result set efficiently
- The cursor can be used to display the results to the user.
Related concept
The related concept documentation is in Android Developer Fundamentals: Concepts.
Learn more
Developer Documentation:
